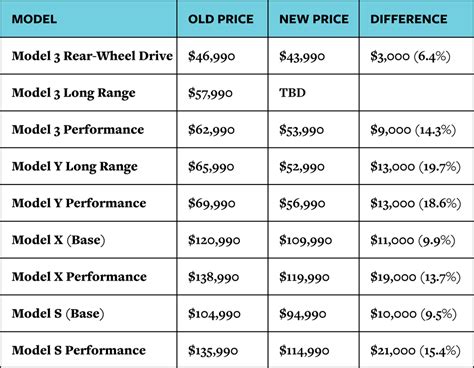
Tesla is reportedly resorting to price cuts and other incentives to boost sales of its existing models, fueling speculation that demand may be softening amid a lineup that hasn’t seen a major refresh in several years. With consumers increasingly drawn to newer electric vehicle offerings from competitors, the electric car giant faces the challenge of maintaining its market dominance.
Tesla is employing various strategies to stimulate demand for its current vehicle lineup, including the Model 3 and Model Y, which have remained largely unchanged for several years. These efforts come as the broader electric vehicle market becomes increasingly competitive, with numerous automakers launching their own EVs, often incorporating the latest technologies and designs. The company’s strategy includes offering discounts and incentives to potential buyers, a tactic that could impact Tesla’s profit margins but is deemed necessary to keep sales volume high.
“They’re using the tools available to them to try to boost sales,” said Gene Munster, managing partner at Deepwater Asset Management, highlighting the company’s proactive approach. The price adjustments and incentives are viewed as a response to a changing market landscape where consumers have more choices than ever before. Munster also stated, “It’s an indication that demand is less than production.”
One specific incentive being offered, as reported by Bloomberg, involves providing six months of free supercharging to new buyers. This perk, which can save drivers a significant amount of money on electricity costs, is designed to make Tesla vehicles more attractive compared to rival EVs. In addition to this, Tesla is also focusing on its referral program, offering rewards to existing owners who successfully refer new customers. These rewards can range from merchandise to access to exclusive events and even enhanced vehicle features.
The pressure on Tesla to maintain its sales numbers is amplified by its ambitious production goals. The company has invested heavily in expanding its manufacturing capacity, including the construction of new Gigafactories in various locations around the world. To justify these investments and maintain profitability, Tesla needs to ensure that its production output is matched by sufficient demand. Failure to do so could lead to inventory buildup and financial strain.
Analysts have noted that the lack of significant updates to Tesla’s core models is a contributing factor to the potential slowdown in sales growth. While the Model 3 and Model Y remain popular choices, they have been on the market for several years without a major redesign. In the fast-paced automotive industry, where new models and technologies are constantly being introduced, this can put a strain on demand. Consumers are often drawn to the latest features and styling, and Tesla’s aging lineup may be losing some of its appeal.
Moreover, the increasing availability of compelling electric vehicles from other manufacturers is further intensifying the competition. Automakers such as Ford, General Motors, Hyundai, and Rivian are all launching EVs that directly compete with Tesla’s offerings. These vehicles often boast unique designs, advanced technologies, and competitive pricing, giving consumers more options to choose from. As a result, Tesla can no longer rely solely on its brand recognition and early-mover advantage to drive sales.
The company’s stock performance has also been under scrutiny, reflecting investor concerns about its growth prospects. While Tesla remains a dominant player in the EV market, its high valuation is predicated on the assumption of continued rapid growth. Any signs of slowing demand or increased competition can trigger a sell-off in its shares.
Looking ahead, Tesla is expected to introduce new models and technologies to reinvigorate its sales. The Cybertruck, an all-electric pickup truck, is slated to begin production, although delays have plagued its development. Additionally, the company is working on a next-generation vehicle platform that could underpin a new range of more affordable EVs. These new offerings are seen as crucial to Tesla’s long-term growth and its ability to maintain its leadership position in the electric vehicle market.
The current situation highlights the challenges faced by even the most successful companies in dynamic industries. Tesla’s need to resort to price cuts and incentives underscores the importance of continuous innovation and adaptation in the face of evolving market conditions and increasing competition. The company’s future success will depend on its ability to develop and launch compelling new products that capture the imagination of consumers and solidify its position as a leader in the electric vehicle revolution.
The moves by Tesla indicate a broader shift in the EV market. Early adopters who were willing to pay a premium for electric vehicles are now largely accounted for, and the industry is moving towards mass-market adoption. This requires automakers to offer more affordable and compelling EVs to appeal to a wider range of consumers. Tesla’s price cuts and incentives reflect this trend, as the company aims to attract new buyers who may be more price-sensitive and less brand-loyal.
Tesla’s Q1 2024 vehicle production and delivery numbers showed deliveries missed analysts’ estimates. The company delivered 386,810 vehicles, below the expected 449,080. Production also disappointed at 433,371 vehicles. This resulted in a 8.5% year-over-year drop from the first quarter of 2023, and a steeper 20.1% plunge compared to the prior quarter.
According to Bloomberg, Troy Teslike, known for his Tesla projections, predicted that the first-quarter deliveries would be closer to 410,000 vehicles.
Tesla cited several reasons for the delivery slump, including production ramp-up of the updated Model 3 at the Fremont factory and factory shutdowns resulting from shipping diversions caused by the conflict in the Red Sea and a fire at Gigafactory Berlin.
However, analysts suggest other factors are at play, including increased competition in China and fading demand for Tesla’s older models. “Tesla is experiencing weaker demand, especially in China, and is facing increasing competition from local EV makers like BYD,” said Dan Ives, an analyst at Wedbush Securities. “The company needs to introduce new models and technologies to reignite growth.”
In addition to price cuts and incentives, Tesla is also focusing on improving its customer service and expanding its charging infrastructure. The company has been criticized in the past for long wait times for service appointments and a lack of charging stations in certain areas. Addressing these issues is seen as crucial to improving customer satisfaction and driving repeat business.
The push to increase sales also coincides with a period of increased scrutiny of Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) technologies. Regulatory agencies are investigating several accidents involving these systems, and there are concerns about their safety and reliability. Tesla is working to improve these technologies and address the concerns of regulators and consumers. However, the ongoing scrutiny could potentially impact sales if consumers become hesitant to purchase vehicles equipped with these features.
Tesla’s strategy also involves expanding into new markets and segments. The company is planning to launch its vehicles in new countries and is developing new models to appeal to different types of customers. For example, the Cybertruck is aimed at the pickup truck market, which is one of the largest and most lucrative segments in the automotive industry. By expanding its reach, Tesla hopes to diversify its revenue streams and reduce its reliance on its existing models and markets.
The company’s energy business, which includes solar panels and energy storage systems, is also playing an increasingly important role in its overall strategy. Tesla is aiming to become a leading provider of clean energy solutions, and it sees its energy business as a key driver of long-term growth. The company is investing heavily in expanding its energy production and storage capacity, and it is developing new products and services to meet the growing demand for clean energy.
The situation also highlights the importance of brand perception in the automotive industry. Tesla has built a strong brand image as an innovative and technologically advanced company. However, this image can be easily tarnished by negative publicity or product failures. Tesla needs to carefully manage its brand reputation to maintain its appeal to consumers and investors.
In conclusion, Tesla’s current sales strategy reflects the evolving dynamics of the electric vehicle market. As competition intensifies and consumer preferences change, the company is adapting its approach to maintain its market share and drive growth. The success of these efforts will depend on Tesla’s ability to innovate, improve customer satisfaction, and effectively manage its brand reputation. The coming months will be crucial in determining whether Tesla can successfully navigate these challenges and solidify its position as a leader in the electric vehicle revolution.
Expanded Analysis and Background Information:
The current predicament Tesla faces is multifaceted, encompassing broader economic trends, evolving consumer behavior, and the intensification of competition within the electric vehicle sector. To fully understand Tesla’s recent strategic moves, it’s crucial to examine these elements in detail.
Economic Factors:
Global economic conditions play a significant role in the automotive market. High interest rates, inflation, and economic uncertainty can all impact consumer spending on big-ticket items like cars. In many markets, interest rates have risen substantially, making auto loans more expensive and potentially deterring consumers from purchasing new vehicles. Inflation also erodes purchasing power, forcing consumers to prioritize essential goods and services over discretionary purchases.
Furthermore, concerns about a potential recession can further dampen consumer sentiment and lead to a decline in auto sales. When economic uncertainty is high, consumers tend to postpone major purchases and save their money instead. This can create a challenging environment for automakers, who need to maintain sales volume to support their operations and investments.
Evolving Consumer Behavior:
Consumer preferences in the automotive market are constantly evolving. Factors such as environmental awareness, technological advancements, and changing lifestyles all influence what consumers look for in a vehicle.
The growing awareness of climate change and the environmental impact of gasoline-powered cars has fueled the demand for electric vehicles. Consumers are increasingly seeking out EVs as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Technological advancements are also playing a key role in shaping consumer preferences. Features such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, and connectivity features are becoming increasingly important to car buyers. Consumers are looking for vehicles that offer the latest technologies and provide a seamless driving experience.
Changing lifestyles are also influencing consumer preferences. For example, the rise of urbanization and the increasing number of people living in cities have led to a greater demand for smaller, more fuel-efficient vehicles. Consumers who live in urban areas often face limited parking space and traffic congestion, making smaller cars a more practical choice.
Competitive Landscape:
The electric vehicle market has become increasingly competitive in recent years. Tesla, which once enjoyed a near-monopoly in the EV space, now faces competition from a growing number of automakers, both established players and new entrants.
Traditional automakers such as Ford, General Motors, Volkswagen, and Toyota are all investing heavily in electric vehicles and launching their own EVs to compete with Tesla. These companies have a long history of manufacturing cars and a well-established dealer network, giving them a significant advantage over Tesla in terms of production capacity and customer reach.
In addition to the traditional automakers, there are also a number of new entrants in the EV market, such as Rivian, Lucid, and Polestar. These companies are focused solely on electric vehicles and are bringing innovative technologies and designs to the market. They are also targeting niche segments of the EV market, such as luxury EVs and electric pickup trucks.
The increased competition in the EV market is putting pressure on Tesla to innovate and improve its products and services. Tesla needs to continue to develop new technologies, improve its manufacturing processes, and offer compelling incentives to maintain its market share and attract new customers.
Tesla’s Specific Challenges:
In addition to the broader economic and competitive challenges, Tesla also faces some specific challenges of its own.
One of the main challenges is the aging of its core models. The Model 3 and Model Y, which account for the majority of Tesla’s sales, have been on the market for several years without a major redesign. In the fast-paced automotive industry, where new models and technologies are constantly being introduced, this can put a strain on demand.
Another challenge is the increasing scrutiny of Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) technologies. Regulatory agencies are investigating several accidents involving these systems, and there are concerns about their safety and reliability. This could potentially impact sales if consumers become hesitant to purchase vehicles equipped with these features.
Tesla is also facing challenges in scaling up production of its new models, such as the Cybertruck. Delays in production can lead to lost sales and damage the company’s reputation. Tesla needs to effectively manage its production processes and ensure that it can meet the demand for its new models.
Finally, Tesla is facing challenges in maintaining its brand image. The company has been criticized in the past for quality issues, customer service problems, and controversial statements by its CEO, Elon Musk. Tesla needs to carefully manage its brand reputation to maintain its appeal to consumers and investors.
Tesla’s Response:
Tesla is responding to these challenges with a variety of strategies, including price cuts, incentives, new models, and improved customer service.
Price cuts and incentives are designed to make Tesla vehicles more affordable and attractive to consumers. These tactics can help to boost sales volume and maintain market share.
New models, such as the Cybertruck and the next-generation vehicle platform, are designed to reinvigorate sales and attract new customers. These new offerings are seen as crucial to Tesla’s long-term growth and its ability to maintain its leadership position in the electric vehicle market.
Improved customer service is designed to address past criticisms and improve customer satisfaction. Tesla is investing in expanding its service network and improving its communication with customers.
The Future Outlook:
The future of Tesla depends on its ability to successfully navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities in the electric vehicle market. Tesla needs to continue to innovate, improve its products and services, and effectively manage its brand reputation.
The electric vehicle market is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the coming years, driven by factors such as increasing environmental awareness, government regulations, and technological advancements. Tesla is well-positioned to benefit from this growth, but it will need to overcome the challenges it faces to maintain its leadership position.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions):
-
Why is Tesla cutting prices on its vehicles?
- Tesla is cutting prices and offering incentives, like six months of free supercharging, to boost sales and manage inventory amid increasing competition in the electric vehicle market and potentially softening demand for its existing models. The move is aimed at attracting price-sensitive consumers and maintaining sales volume, particularly as the Model 3 and Model Y have not seen major redesigns in several years. According to Gene Munster, Managing Partner at Deepwater Asset Management, “They’re using the tools available to them to try to boost sales” which shows the proactive approach of the company.
-
What factors are contributing to the potential slowdown in Tesla’s sales growth?
- Several factors are contributing to the potential slowdown in Tesla’s sales growth: the aging of its existing models (Model 3 and Model Y), which haven’t seen major updates in years; increasing competition from other automakers offering compelling EVs; and broader economic conditions like high interest rates and inflation affecting consumer spending.
-
How does the competition from other EV manufacturers impact Tesla’s market position?
- Increasing competition from established automakers like Ford and GM, as well as new EV companies like Rivian and Lucid, is eroding Tesla’s market share. These competitors offer diverse designs, technologies, and competitive pricing, providing consumers with more choices and reducing Tesla’s reliance on its brand recognition and early-mover advantage.
-
What new models or technologies is Tesla planning to introduce to boost sales?
- Tesla is planning to introduce the Cybertruck, an all-electric pickup truck, and is developing a next-generation vehicle platform that could underpin a new range of more affordable EVs. These new offerings are crucial for Tesla’s long-term growth and ability to maintain its leadership in the EV market.
-
What were the specific reasons Tesla gave for the Q1 2024 delivery slump?
- Tesla cited several reasons for the Q1 2024 delivery slump, including the production ramp-up of the updated Model 3 at the Fremont factory, factory shutdowns due to shipping diversions caused by the conflict in the Red Sea, and a fire at Gigafactory Berlin. However, analysts also suggest increased competition in China and fading demand for Tesla’s older models as contributing factors.