Carmakers, particularly BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz, are bracing for significant price increases on vehicles imported into the United States, potentially impacting consumers and the broader automotive market due to recent tariff escalations and unresolved trade disputes.
The automotive industry is facing a mounting crisis as tariffs threaten to significantly raise the cost of imported vehicles, potentially dampening consumer demand and disrupting established supply chains. BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz are among the brands most exposed to these tariffs, and consumers could see prices jump substantially. The tariffs on automotive parts are already in effect, adding to the manufacturing cost. If additional tariffs are placed on completed vehicles, the impact will be directly felt by car buyers. The price hikes could have a ripple effect, potentially impacting sales volumes and overall market competitiveness for these brands.
According to industry analysts, the tariffs on auto parts and the potential for tariffs on completed vehicles creates a difficult situation. The cost increases could force manufacturers to re-evaluate their pricing strategies, potentially leading to lower profit margins or reduced investment in future technologies. It could also force them to move manufacturing to the U.S.
“This is a very fluid situation, and the ultimate impact will depend on the specific tariffs imposed and how manufacturers respond,” said an analyst. “However, it’s clear that these tariffs pose a significant risk to the automotive industry and could have far-reaching consequences for consumers and the economy.”
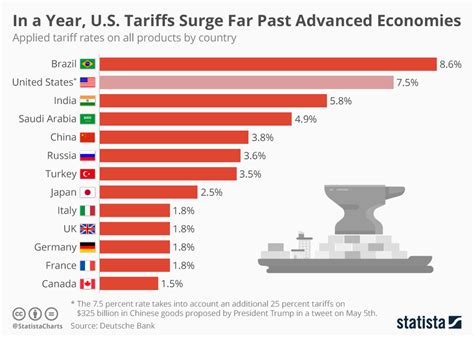
The tariffs affecting the automotive sector stem from ongoing trade disputes between the United States and other major economies, including the European Union and China. These disputes involve a range of issues, including trade imbalances, intellectual property rights, and market access. The U.S. government has argued that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and encourage fair trade practices, while other countries contend that tariffs are protectionist measures that disrupt global trade and harm consumers.
The imposition of tariffs on imported vehicles and auto parts has been a contentious issue within the automotive industry. Some manufacturers have warned that tariffs could lead to job losses, reduced investment, and higher prices for consumers. Others have argued that tariffs could encourage domestic production and create new opportunities for U.S. companies. However, the overall consensus within the industry is that tariffs are detrimental to global trade and could have negative consequences for the automotive market.
The potential for price increases is a major concern for consumers, who may be forced to delay or forego purchasing new vehicles if prices become too high. This could lead to a slowdown in auto sales and a decline in overall economic activity. Moreover, higher prices for imported vehicles could make domestic vehicles more competitive, potentially shifting consumer demand towards U.S.-made cars and trucks. However, even domestic manufacturers rely on imported parts, so they are not immune to the effects of tariffs on auto parts.
BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz are particularly vulnerable to tariffs due to their significant import volumes into the United States. These brands rely heavily on production facilities in Europe and other regions to supply the U.S. market. If tariffs are imposed on imported vehicles, these manufacturers could face substantial cost increases, which could force them to raise prices or absorb the losses.
BMW has a large manufacturing plant in South Carolina, but it also imports a significant number of vehicles from Europe. Volkswagen has a plant in Tennessee, but it also imports many vehicles from Germany and Mexico. Mercedes-Benz has a plant in Alabama, but it also imports a significant number of vehicles from Germany.
“We are closely monitoring the situation and assessing the potential impact on our business,” said a spokesperson for BMW. “We remain committed to providing our customers with high-quality vehicles at competitive prices, but we may need to adjust our pricing strategy if tariffs are imposed.”
Volkswagen and Mercedes-Benz have also expressed concerns about the potential impact of tariffs on their businesses.
The effects of tariffs extend beyond the immediate price increases for consumers and manufacturers. The automotive industry is a complex global network, and tariffs can disrupt established supply chains, create uncertainty for investors, and lead to retaliatory measures from other countries. These factors can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, impacting a wide range of industries and sectors.
For example, tariffs on auto parts could affect suppliers of raw materials, components, and manufacturing equipment. These suppliers may be forced to raise prices, reduce production, or even close down operations. Similarly, tariffs on completed vehicles could affect dealerships, transportation companies, and other businesses that rely on the automotive industry.
The long-term consequences of tariffs on the automotive industry are uncertain, but experts warn that they could have lasting effects on the global economy. Tariffs could lead to a fragmentation of global trade, a decline in international cooperation, and a rise in protectionism. These factors could undermine economic growth and stability and make it more difficult for countries to address global challenges.
“The automotive industry is a vital engine of economic growth and innovation,” said an economist. “Tariffs pose a significant threat to this industry and could have far-reaching consequences for the global economy. It is essential that policymakers find a way to resolve these trade disputes and avoid a trade war.”
The automotive industry is closely watching the situation and hoping for a resolution that will avoid the imposition of tariffs. However, in the meantime, manufacturers are preparing for the worst and exploring ways to mitigate the potential impact on their businesses.
Detailed Breakdown of Potential Impacts and Contributing Factors
The potential ramifications of increased tariffs on the automotive industry extend far beyond simple price hikes for consumers. They encompass a complex web of interconnected factors that could reshape the industry landscape and have lasting economic consequences. To fully grasp the potential impact, it’s crucial to delve into the specific areas most affected:
- Consumer Impact: The most immediate and visible effect of tariffs will be higher prices for imported vehicles. This will disproportionately impact consumers who prefer or rely on foreign brands, potentially forcing them to reconsider their purchasing decisions. Consumers may opt for less expensive vehicles, delay purchases, or turn to the used car market. The potential decrease in demand could hurt sales volumes for affected brands, leading to lower revenues and profits. Furthermore, even for consumers who ultimately purchase an imported vehicle despite the higher price, their purchasing power will be diminished, potentially impacting spending in other areas of the economy.
- Manufacturer Strategies: Car manufacturers facing increased tariffs have several strategic options, each with its own set of trade-offs. They could absorb the increased costs themselves, accepting lower profit margins to maintain sales volume. This strategy is likely unsustainable in the long run, especially if tariffs remain in place or increase further. Alternatively, they could pass the costs on to consumers through higher prices, risking a decline in sales. Another option is to shift production to the United States to avoid tariffs altogether. However, this requires significant investment and time, and may not be feasible for all models or manufacturers. Finally, manufacturers could seek exemptions from tariffs or lobby for trade agreements that reduce or eliminate tariffs. This approach requires political maneuvering and is subject to uncertainty.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The automotive industry relies on a complex global supply chain, with parts and components sourced from multiple countries. Tariffs on auto parts can disrupt this supply chain, leading to increased costs, delays, and shortages. Manufacturers may be forced to find alternative suppliers, which can be time-consuming and expensive. They may also need to redesign vehicles to accommodate different parts, which can further increase costs. The disruption of the supply chain can also affect the quality and reliability of vehicles.
- Impact on Innovation: The automotive industry is undergoing a period of rapid innovation, with the development of electric vehicles, autonomous driving technology, and connected car services. Tariffs can stifle innovation by increasing costs and reducing investment. Manufacturers may be forced to cut back on research and development spending, delaying the introduction of new technologies. They may also be less willing to take risks and invest in unproven technologies. The long-term consequences of reduced innovation could be a loss of competitiveness for the U.S. automotive industry.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The imposition of tariffs on imported vehicles can have broader geopolitical implications. It can strain relationships between countries, leading to retaliatory measures and trade wars. It can also undermine the rules-based international trading system, creating uncertainty and instability. The potential for geopolitical conflict is a major concern for the automotive industry, which relies on global trade and cooperation.
- The U.S. Manufacturing Paradox: While the stated goal of tariffs is often to encourage domestic manufacturing, the reality is more complex. Many “domestic” manufacturers rely on imported parts and components. Tariffs on these parts can increase their costs, making them less competitive. Moreover, even if tariffs do lead to increased production in the United States, it’s not clear that this will create a significant number of new jobs. Automation and other technological advancements are reducing the need for human labor in manufacturing. It is thus plausible that even with increased production capacity in the US, the benefit of job creation may not materialize.
- Retaliatory Measures: The imposition of tariffs by one country often leads to retaliatory measures by other countries. This can escalate into a trade war, with tariffs imposed on a wide range of goods and services. A trade war can have devastating consequences for the global economy, disrupting trade flows, reducing investment, and increasing prices for consumers. The automotive industry is particularly vulnerable to a trade war, as it relies on global trade and investment. The retaliatory tariffs may target the United States automotive exports, which will undermine the intended benefit of the initial tariffs.
- Currency Fluctuations: Tariffs can also affect currency exchange rates. If a country imposes tariffs on imports, its currency may appreciate. This can make its exports more expensive and its imports cheaper, offsetting the intended effects of the tariffs. Currency fluctuations can also create uncertainty for businesses, making it more difficult to plan and invest. Therefore, manufacturers will have a difficult time in planning their financial strategies.
The Case of BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz: A Deeper Look
To understand the specific challenges faced by BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz, it’s important to examine their individual business models and their reliance on imported vehicles.
- BMW: BMW has a significant manufacturing presence in the United States, with a plant in South Carolina that produces a range of models, including SUVs. However, the company also imports a significant number of vehicles from Europe, particularly its sedans, coupes, and convertibles. These imported vehicles are particularly vulnerable to tariffs. BMW has warned that tariffs could lead to higher prices for consumers and reduced investment in the United States. They also warned of potential job losses in the U.S.
- Volkswagen: Volkswagen has a plant in Tennessee that produces the Passat and the Atlas. However, the company also imports a large number of vehicles from Germany and Mexico, including the Golf, the Jetta, and the Tiguan. These imported vehicles are also vulnerable to tariffs. Volkswagen has expressed concerns about the potential impact of tariffs on its business and has called for a resolution to the trade disputes. Volkswagen also has invested heavily in EV technologies, which could be undermined by the increased cost.
- Mercedes-Benz: Mercedes-Benz has a plant in Alabama that produces SUVs. However, the company also imports a significant number of vehicles from Germany, including its sedans, coupes, and convertibles. These imported vehicles are also vulnerable to tariffs. Mercedes-Benz has expressed concerns about the potential impact of tariffs on its business and has called for a level playing field in international trade.
These three manufacturers are particularly vulnerable to tariffs because they rely heavily on imported vehicles to satisfy demand in the United States. If tariffs are imposed, they will face difficult choices about how to respond. They may be forced to raise prices, reduce investment, or shift production to the United States. All of these options would have negative consequences for their businesses and for the U.S. economy.
The issue is not just about the immediate increase in cost, but the potential long-term damage to their brand value if their vehicles become perceived as unaffordable due to tariff-induced price hikes. This is especially concerning in the luxury segment, where brand image and perceived value are critical factors in consumer purchasing decisions.
The Role of Government and Potential Policy Solutions
Addressing the challenges posed by tariffs requires a multifaceted approach involving both government and industry stakeholders. Potential policy solutions include:
- Negotiating Trade Agreements: The most effective way to resolve trade disputes and avoid tariffs is to negotiate comprehensive trade agreements that address the underlying issues. These agreements should aim to reduce trade barriers, promote fair trade practices, and protect intellectual property rights. Negotiations with the EU and China could significantly alleviate the tariff pressure on the automotive industry.
- Providing Tariff Exemptions: In certain cases, the government may grant tariff exemptions to specific companies or products. This can provide temporary relief from the negative effects of tariffs. However, exemptions should be carefully targeted and should not undermine the overall goals of trade policy.
- Investing in Domestic Manufacturing: The government can support domestic manufacturing by investing in infrastructure, workforce training, and research and development. This can help to make U.S. manufacturers more competitive and reduce their reliance on imported parts and components.
- Supporting Innovation: The government can promote innovation by providing tax incentives, grants, and other forms of support for research and development. This can help to ensure that the U.S. automotive industry remains at the forefront of technological advancements.
- Monitoring and Enforcing Trade Laws: The government should actively monitor and enforce trade laws to ensure that all countries are playing by the rules. This can help to prevent unfair trade practices, such as dumping and subsidies, which can harm U.S. manufacturers.
Conclusion
The potential for increased tariffs on imported vehicles poses a significant threat to the automotive industry, with potentially far-reaching consequences for consumers, manufacturers, and the global economy. BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz are particularly vulnerable to these tariffs, and they may be forced to raise prices, reduce investment, or shift production to the United States. Addressing the challenges posed by tariffs requires a multifaceted approach involving both government and industry stakeholders. By negotiating trade agreements, providing tariff exemptions, investing in domestic manufacturing, supporting innovation, and monitoring and enforcing trade laws, it is possible to mitigate the negative effects of tariffs and ensure that the U.S. automotive industry remains competitive in the global market. Failure to do so could result in higher prices for consumers, reduced innovation, and a decline in economic activity. This could also affect the consumers’ choice of new energy vehicles (NEV) and other alternative energy options because the traditional car industry will need to increase their cost, making alternative energy options more competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the main reasons behind the potential tariff increases on imported vehicles?
The potential tariff increases are primarily due to ongoing trade disputes between the United States and other major economies, including the European Union and China. These disputes involve issues such as trade imbalances, intellectual property rights, and market access. The U.S. government has argued that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and encourage fair trade practices.
2. Which car brands are likely to be most affected by the tariff increases and why?
BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz are among the brands most exposed to potential tariff increases. This is because they rely heavily on production facilities in Europe and other regions to supply the U.S. market, importing a significant number of vehicles. Any tariffs imposed on imported vehicles would disproportionately affect these manufacturers.
3. How might these tariffs impact consumers in the United States?
Consumers could face significantly higher prices for imported vehicles if tariffs are implemented. This could lead to a decrease in demand for these vehicles, as consumers may delay purchases, opt for less expensive alternatives, or turn to the used car market. Reduced consumer spending on new cars could have broader economic implications.
4. What strategies can car manufacturers adopt to mitigate the negative effects of these tariffs?
Car manufacturers have several options, including absorbing the increased costs (reducing profit margins), passing the costs on to consumers (raising prices), shifting production to the United States (requiring significant investment), seeking tariff exemptions, or lobbying for trade agreements that reduce or eliminate tariffs. Each strategy has its own trade-offs and challenges.
5. What are the potential long-term consequences of these tariffs for the automotive industry and the global economy?
The long-term consequences could include disruptions to global supply chains, reduced investment in innovation, strained relationships between countries, and a potential rise in protectionism. A trade war could lead to a fragmentation of global trade, a decline in international cooperation, and undermine economic growth and stability. There may also be an impact in currency rates as trade between nations are affected.



![[Restaurant Name] Returns! Iconic Chain Revives After 30-Year Absence](https://generasitekno.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/unnamed-file-924-150x150.jpg)