A massive data breach has exposed millions of passwords, prompting urgent warnings to U.S. consumers to check if their accounts have been compromised. Cybersecurity experts are urging individuals to take immediate action to protect themselves against potential fraud and identity theft following the discovery of a vast collection of compromised credentials circulating online. The breach underscores the persistent threat of cyberattacks and the importance of practicing robust password hygiene.
Millions of Passwords Exposed in Massive Data Breach
A significant data breach has put millions of U.S. consumers at risk, with compromised passwords now circulating online. Cybersecurity experts are issuing urgent warnings, urging individuals to take immediate steps to determine if their accounts have been affected and to secure their online presence. The breach highlights the ongoing vulnerability of online accounts and the critical need for strong password practices.
The leaked data encompasses a wide range of online accounts, potentially affecting individuals’ access to email, social media, banking, and other sensitive services. According to cybersecurity analysts, the breach appears to be the result of several separate incidents, aggregated into a single, massive collection of compromised credentials. “This is a significant event that could have far-reaching consequences for individuals and organizations alike,” stated a lead analyst from a prominent cybersecurity firm.
The scale of the breach is still being assessed, but initial findings suggest that millions of unique passwords and usernames have been exposed. The compromised data includes not only login credentials but also potentially other personal information, such as email addresses, phone numbers, and security questions. This information could be used by malicious actors to conduct a variety of cybercrimes, including identity theft, financial fraud, and phishing attacks.
Urgent Recommendations for Consumers
In light of the massive breach, cybersecurity experts are recommending that consumers take the following immediate steps to protect themselves:
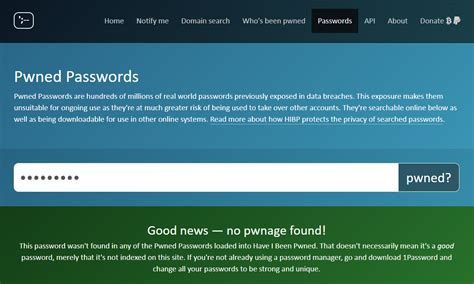
- Check if Your Accounts Have Been Compromised: Use online tools and resources to determine if your email address or username has been involved in a known data breach. Several websites, such as Have I Been Pwned (HIBP), allow users to enter their email address or username and check if it appears in a database of known breaches.
- Change Your Passwords Immediately: If your accounts have been compromised, change your passwords immediately. Choose strong, unique passwords for each of your online accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords, such as your name, birthday, or common words.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your online accounts. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attacks: Be vigilant about phishing emails and other scams that may attempt to trick you into revealing your personal information. Do not click on links or open attachments from unknown senders.
- Monitor Your Credit Report: Monitor your credit report regularly for any signs of fraud or identity theft. You can obtain a free copy of your credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) once a year.
The Importance of Strong Password Practices
The recent data breach underscores the importance of strong password practices. Many people still use weak or easily guessable passwords, making their accounts vulnerable to attack. Cybersecurity experts recommend the following tips for creating strong passwords:
- Use a Combination of Characters: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Make It Long: Aim for passwords that are at least 12 characters long.
- Avoid Personal Information: Do not use your name, birthday, or other personal information in your passwords.
- Use Unique Passwords for Each Account: Do not reuse the same password for multiple accounts. If one account is compromised, all accounts that use the same password will be vulnerable.
- Use a Password Manager: Consider using a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords for all of your accounts. Password managers can also help you keep track of your passwords and automatically fill them in when you log in to websites.
The Role of Organizations in Protecting User Data
While individual users have a responsibility to protect their own accounts, organizations also have a critical role to play in protecting user data. Organizations should implement strong security measures to protect their systems from attack and to prevent data breaches. These measures should include:
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems.
- Employee Training: Provide employees with training on cybersecurity best practices.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement an incident response plan to address data breaches and other security incidents.
“Organizations must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity and invest in the tools and resources necessary to protect user data,” said a cybersecurity consultant. “Data breaches can have a devastating impact on organizations, both financially and reputationally.”
The Broader Implications of Data Breaches
Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, and they have significant implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. In addition to the direct financial costs of data breaches, such as the cost of remediation and legal fees, there are also indirect costs, such as the loss of customer trust and the damage to an organization’s reputation.
Data breaches can also lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other cybercrimes. Individuals whose personal information has been compromised in a data breach may be at risk of having their credit cards stolen, their bank accounts emptied, or their identities used to commit crimes.
The increasing frequency and severity of data breaches are raising concerns about the security of the internet and the protection of personal data. Governments and organizations are working to develop new laws and regulations to address these concerns, but more needs to be done to protect individuals and organizations from the threat of cybercrime.
Government and Industry Response
In the wake of this and other recent data breaches, government agencies and industry organizations are stepping up their efforts to combat cybercrime and protect consumer data. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is actively investigating data breaches and taking enforcement actions against companies that fail to protect consumer data. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed cybersecurity standards and guidelines to help organizations improve their security posture.
Industry organizations are also working to develop best practices for data security and to share information about emerging threats. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) provides a range of cybersecurity resources and tools, including security benchmarks and configuration guidelines.
“Collaboration between government, industry, and individuals is essential to effectively combat cybercrime and protect data,” said a government cybersecurity official. “We must work together to raise awareness of the risks and to develop and implement effective security measures.”
Long-Term Strategies for Cybersecurity
Addressing the growing threat of data breaches and cybercrime requires a long-term, multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Investing in Cybersecurity Research and Development: Investing in research and development to develop new cybersecurity technologies and strategies.
- Improving Cybersecurity Education and Training: Improving cybersecurity education and training for individuals, organizations, and government agencies.
- Strengthening International Cooperation: Strengthening international cooperation to combat cybercrime and to share information about emerging threats.
- Promoting a Culture of Cybersecurity Awareness: Promoting a culture of cybersecurity awareness among individuals and organizations.
By taking these steps, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and protect ourselves from the growing threat of cybercrime. The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and cybersecurity efforts must adapt to meet the challenges of this dynamic environment. A proactive and vigilant approach is essential to safeguarding personal and organizational data in the face of increasing cyber threats.
Quote from Yahoo News Article:
The Yahoo News article quotes the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) as saying, “CISA encourages users to use strong passwords, and if feasible, use multi-factor authentication.” This emphasizes the need for individuals to enhance their security measures to protect against potential cyber threats.
FAQ: Massive Password Breach
1. How do I know if my password has been compromised in this breach?
You can check if your email address or username has been involved in a known data breach by using online tools like Have I Been Pwned (HIBP). Simply enter your email or username on the site, and it will check against a database of known breaches. If your information appears in the results, your password may have been compromised.
2. What should I do immediately if I find out my password was part of the breach?
If you discover that your password was involved in the breach, change it immediately. Additionally, if you used that same password for other accounts, change it on those accounts as well. Choose a strong, unique password for each account to minimize the risk of future breaches.
3. What makes a password “strong” and difficult to crack?
A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using personal information such as your name, birthday, or common words that can be easily guessed. It’s also essential to create unique passwords for each of your online accounts.
4. What is two-factor authentication (2FA) and how does it help protect my accounts?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts. When enabled, you’ll need to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or generated by an authenticator app, in addition to your password. This makes it much harder for unauthorized individuals to access your account, even if they have your password.
5. Besides changing my password, what other steps can I take to protect myself from potential harm after a data breach?
In addition to changing your password and enabling 2FA, be cautious of phishing emails and scams that may try to trick you into revealing personal information. Monitor your credit report regularly for any signs of fraud or identity theft. Consider using a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. Keeping your software and devices up to date with the latest security patches can also help protect against vulnerabilities.
Expanded Analysis: The Anatomy of a Data Breach and Its Aftermath
Data breaches have become a pervasive threat in the digital age, impacting individuals, organizations, and governments alike. Understanding the anatomy of a data breach, its potential causes, and the steps that can be taken in its aftermath is crucial for mitigating risks and minimizing the damage caused by such incidents.
The Anatomy of a Data Breach:
-
The Initial Intrusion: Data breaches often begin with a cyberattack targeting vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems. Common attack vectors include:
- Phishing Attacks: Malicious emails or messages designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
- Malware Infections: Viruses, worms, or other malicious software that can compromise systems and steal data.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Hackers may exploit known vulnerabilities in software or hardware to gain unauthorized access.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or granting access to systems.
- Data Exfiltration: Once attackers have gained access to a system, they may attempt to exfiltrate sensitive data. This can involve copying files, databases, or other information and transferring it to an external location.
- Discovery and Containment: Organizations may discover a data breach through various means, such as security alerts, incident reports, or external notifications. Once a breach is discovered, the focus shifts to containing the damage and preventing further data loss.
- Investigation and Remediation: Following containment, a thorough investigation is conducted to determine the scope of the breach, identify the affected data, and assess the root cause. Remediation efforts involve patching vulnerabilities, strengthening security controls, and implementing measures to prevent future incidents.
- Notification and Disclosure: Depending on the nature of the data breach and applicable laws and regulations, organizations may be required to notify affected individuals, regulators, and law enforcement agencies.
- Recovery and Restoration: The final stage involves restoring systems to their pre-breach state, rebuilding trust with customers and stakeholders, and implementing long-term strategies to enhance cybersecurity posture.
Causes of Data Breaches:
Data breaches can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Weak Passwords: Using easily guessable or commonly used passwords makes accounts vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- Lack of Security Awareness: Insufficient training and awareness among employees can lead to human errors that compromise security.
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Failure to promptly patch software vulnerabilities creates opportunities for attackers to exploit weaknesses.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent insiders can intentionally or unintentionally expose sensitive data.
- Inadequate Security Controls: Weak or missing security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, can make it easier for attackers to penetrate systems.
- Complex IT Environments: Complex IT environments with numerous interconnected systems can be difficult to secure and manage, increasing the risk of vulnerabilities.
Steps to Take After a Data Breach:
-
Immediate Actions:
- Isolate Affected Systems: Immediately isolate compromised systems to prevent the spread of malware or further data loss.
- Change Passwords: Reset passwords for all affected accounts and implement strong password policies.
- Notify Stakeholders: Notify affected individuals, regulators, and law enforcement agencies as required by applicable laws and regulations.
- Engage Experts: Engage cybersecurity experts to assist with incident response, investigation, and remediation efforts.
-
Investigation and Analysis:
- Conduct Forensic Analysis: Conduct a thorough forensic analysis to determine the scope of the breach, identify the affected data, and assess the root cause.
- Review Security Logs: Analyze security logs to identify suspicious activity and track the attacker’s movements.
- Assess Vulnerabilities: Assess vulnerabilities in systems and applications and prioritize remediation efforts.
-
Remediation and Recovery:
- Patch Vulnerabilities: Promptly patch software vulnerabilities and implement security updates.
- Strengthen Security Controls: Implement or enhance security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls.
- Improve Security Awareness: Provide security awareness training to employees to promote safe computing practices.
- Restore Data: Restore data from backups if necessary, ensuring that backups are clean and free from malware.
-
Long-Term Strategies:
- Develop Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement a comprehensive incident response plan to guide actions in the event of a future data breach.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in systems and processes.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization.
- Continuously Monitor Systems: Continuously monitor systems and networks for suspicious activity and emerging threats.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and trends and adapt security measures accordingly.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in Combating Data Breaches
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain are playing an increasingly important role in combating data breaches and enhancing cybersecurity.
- AI and ML for Threat Detection: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies, identify suspicious activity, and predict potential threats. These technologies can automate threat detection, improve accuracy, and reduce response times.
- Blockchain for Data Security: Blockchain technology can be used to create immutable records of transactions and data, enhancing data integrity and security. Blockchain can be used for identity management, access control, and secure data storage.
- Automation for Incident Response: Automation tools can streamline incident response processes, enabling organizations to quickly contain and remediate data breaches. Automation can be used for tasks such as isolating affected systems, patching vulnerabilities, and notifying stakeholders.
The Importance of a Proactive Approach to Cybersecurity
In today’s threat landscape, a proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential for protecting data and preventing data breaches. This involves implementing a layered security approach, continuously monitoring systems, and adapting security measures to address emerging threats. By taking a proactive approach, organizations can reduce their risk of data breaches and minimize the damage caused by such incidents.
The ongoing battle against cybercrime requires constant vigilance, adaptation, and a commitment to implementing robust security measures. As technology continues to evolve, so too must the strategies and tools used to protect data and prevent breaches. By staying informed, investing in cybersecurity, and working together, individuals, organizations, and governments can mitigate the risks and build a more secure digital future.