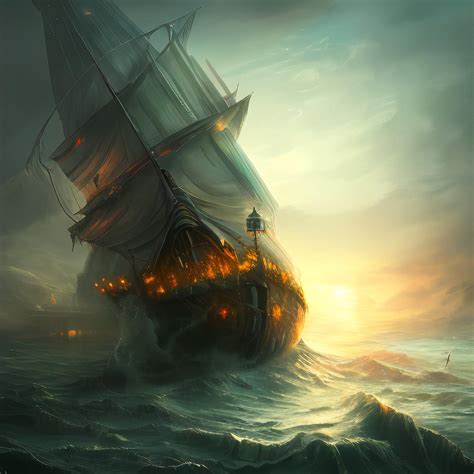
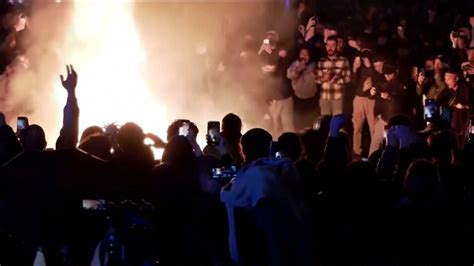A cargo ship adrift in the Pacific Ocean and laden with thousands of electric vehicles (EVs) is ablaze, raising concerns about a potential environmental disaster. The vessel, the Felicity Ace, was abandoned in mid-February after a fire erupted, and despite salvage efforts, the blaze continues to burn intensely. Authorities are monitoring the situation closely, fearing the toxic fumes and potential for a large-scale oil spill could cause significant harm to marine life and the surrounding ecosystem.
The Felicity Ace, a car carrier en route from Emden, Germany (near Volkswagen’s headquarters), to Davisville, Rhode Island, caught fire on February 16 approximately 220 nautical miles (253 miles, 407 km) southwest of the Azores, a Portuguese archipelago. The ship was carrying approximately 4,000 vehicles, including models from Volkswagen, Porsche, Audi, Bentley, and Lamborghini. The exact cause of the fire remains under investigation, but initial reports suggested that lithium-ion batteries in the electric vehicles on board may have contributed to the intensity and persistence of the blaze.
All 22 crew members were safely evacuated from the vessel by the Portuguese Navy, with assistance from commercial ships in the area. No injuries or fatalities were reported. However, the fate of the vehicles, estimated to be worth hundreds of millions of dollars, and the environmental implications of the burning ship are now the primary concerns.
The presence of lithium-ion batteries in the EVs onboard has complicated firefighting efforts. Traditional firefighting methods, such as using water, are often ineffective in extinguishing lithium-ion battery fires and can even exacerbate the situation by causing thermal runaway – a chain reaction where heat from one battery cell spreads to adjacent cells, leading to further fires and explosions. “Lithium-ion batteries burn hot and are difficult to extinguish,” explained a maritime safety expert. “They can reignite even after they appear to be extinguished.”
Salvage teams were dispatched to the scene, but the intense heat and unstable condition of the ship made it difficult to approach and assess the situation. Specialized equipment and techniques are required to safely extinguish lithium-ion battery fires, and the remote location of the ship further complicates the salvage operation. “The fire is a major challenge,” stated a spokesperson for the salvage company. “The batteries are adding fuel to the fire, and it’s a very complex situation.”
The environmental risks associated with the burning ship are significant. The combustion of lithium-ion batteries releases toxic fumes, including hydrogen fluoride, which can be harmful to human health and marine life. The potential for a large-scale oil spill is also a major concern, as the ship contains a substantial amount of fuel oil. If the ship were to sink, it could release this fuel into the ocean, causing widespread pollution and damage to the marine ecosystem.
Environmental organizations have expressed concern about the potential long-term impacts of the Felicity Ace incident. “This is a wake-up call,” said a representative from a leading environmental group. “We need to develop better safety regulations for transporting electric vehicles by sea, and we need to be prepared to respond effectively to incidents like this.”
The incident also raises questions about the safety of transporting large quantities of lithium-ion batteries, particularly in the context of the growing popularity of electric vehicles. Regulations governing the transportation of lithium-ion batteries are constantly evolving, but some experts argue that they are not keeping pace with the rapid growth of the EV market. “The current regulations may not be adequate to address the risks associated with transporting thousands of EVs on a single ship,” said a transportation safety analyst. “We need to review and update these regulations to ensure the safety of maritime transport.”
As of late February/early March, the Felicity Ace eventually sank while being towed, increasing the environmental risk substantially. The exact location of the sunken vessel is being monitored, and further environmental impact assessments are planned.
The incident involving the Felicity Ace serves as a stark reminder of the potential risks associated with the transportation of electric vehicles and the need for improved safety measures and emergency response protocols. The incident also highlights the importance of ongoing research and development into safer battery technologies and more effective firefighting techniques.
Expanded Details and Context
The Felicity Ace incident is not an isolated case, but it is one of the most high-profile incidents involving the transport of electric vehicles by sea. There have been other reported incidents of fires on cargo ships carrying lithium-ion batteries, but none have involved such a large number of vehicles or generated such widespread concern.
The growth of the electric vehicle market has led to a significant increase in the number of lithium-ion batteries being transported by sea. These batteries are used in a wide range of applications, including electric cars, electric buses, electric trucks, and energy storage systems. The increasing volume of lithium-ion battery shipments has raised concerns about the potential for more frequent and more severe incidents involving fires and explosions.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO), the United Nations agency responsible for maritime safety and security, has developed regulations for the safe transport of dangerous goods by sea, including lithium-ion batteries. These regulations cover a wide range of topics, including packaging, labeling, stowage, and firefighting. However, some experts argue that the IMO regulations are not comprehensive enough to address the specific risks associated with the transport of large quantities of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles.
One of the key challenges in regulating the transport of lithium-ion batteries is the complexity of the batteries themselves. Lithium-ion batteries come in a variety of different chemistries, sizes, and configurations, and each type of battery has its own unique set of safety characteristics. This makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all set of regulations that adequately addresses the risks associated with all types of lithium-ion batteries.
Another challenge is the rapid pace of technological innovation in the battery industry. New battery technologies are constantly being developed, and it can be difficult for regulators to keep pace with these changes. This means that the regulations governing the transport of lithium-ion batteries may not always reflect the latest state of the art in battery technology.
In addition to the IMO regulations, some countries and regions have developed their own regulations for the transport of lithium-ion batteries. For example, the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) has issued regulations for the transport of lithium-ion batteries by air and by ground. These regulations are generally more stringent than the IMO regulations, and they include requirements for testing, packaging, and labeling.
The Felicity Ace incident has prompted calls for a review of the regulations governing the transport of lithium-ion batteries by sea. Some experts are calling for stricter regulations on the packaging and stowage of lithium-ion batteries, as well as improved firefighting capabilities on cargo ships. Others are calling for more research into safer battery technologies and more effective methods for extinguishing lithium-ion battery fires.
The investigation into the Felicity Ace incident is ongoing. The investigators will be looking at a variety of factors, including the cause of the fire, the effectiveness of the firefighting efforts, and the environmental impact of the incident. The findings of the investigation could lead to changes in the regulations governing the transport of lithium-ion batteries by sea.
The long-term consequences of the Felicity Ace incident are still unknown. The incident could have a significant impact on the electric vehicle industry, as it raises concerns about the safety of transporting EVs by sea. The incident could also lead to changes in the insurance industry, as insurers may be reluctant to cover shipments of EVs in the future.
The Felicity Ace incident is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant implications for the electric vehicle industry, the maritime industry, and the environment. It is important to continue to monitor the situation closely and to learn from the incident in order to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. The incident highlights the need for collaboration between regulators, industry stakeholders, and researchers to develop safer battery technologies, improve firefighting capabilities, and strengthen the regulations governing the transport of lithium-ion batteries.
Environmental Impact in Detail
The potential environmental impact of the Felicity Ace incident is multifaceted and could have long-lasting consequences for the marine ecosystem. Several key areas of concern include:
-
Air Pollution: The burning of the ship and its cargo, including the vehicles and the lithium-ion batteries, released a cocktail of toxic fumes into the atmosphere. These fumes contain harmful substances such as particulate matter, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, which can contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues for marine life and potentially impact air quality in nearby regions depending on wind patterns. The hydrogen fluoride released from burning lithium-ion batteries is particularly corrosive and dangerous.
-
Water Pollution: The fire also posed a significant threat to water quality. The runoff from firefighting efforts, as well as the leaching of chemicals from the burning vehicles and batteries, could contaminate the surrounding waters. This contamination could harm marine organisms, disrupt food chains, and potentially affect human health through the consumption of contaminated seafood. Heavy metals, electrolytes, and other components of lithium-ion batteries can be particularly toxic to marine life.
-
Oil Spill: The Felicity Ace carried a substantial amount of fuel oil, which is used to power the ship’s engines. If the ship were to sink or break apart, this fuel oil could be released into the ocean, causing a large-scale oil spill. Oil spills can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems, smothering marine life, poisoning animals, and disrupting habitats. The cleanup of oil spills is a complex and expensive undertaking.
-
Seabed Contamination: The sinking of the Felicity Ace resulted in the ship and its remaining cargo settling on the seabed. This could lead to long-term contamination of the seabed with heavy metals, plastics, and other pollutants. These pollutants can accumulate in the food chain and have a detrimental effect on marine life. The physical presence of the wreckage can also disrupt marine habitats and interfere with fishing activities.
-
Plastic Pollution: Vehicles contain a significant amount of plastic components, which can break down into microplastics over time. These microplastics can enter the marine food chain and accumulate in marine organisms, potentially harming their health and disrupting ecosystem functions. Microplastic pollution is a growing concern worldwide, and incidents like the Felicity Ace can contribute to this problem.
-
Impact on Marine Life: The combination of air pollution, water pollution, oil spills, and seabed contamination can have a severe impact on marine life. Fish, marine mammals, seabirds, and other marine organisms can be directly exposed to pollutants, leading to illness, injury, or death. The disruption of food chains can also have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Sensitive habitats, such as coral reefs and seagrass beds, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of pollution.
-
Long-Term Effects: The long-term environmental effects of the Felicity Ace incident are difficult to predict with certainty. However, it is likely that the incident will have a lasting impact on the marine ecosystem in the area. Monitoring and remediation efforts will be necessary to assess the extent of the damage and to mitigate the long-term effects of the incident.
Environmental agencies and organizations are working to assess the environmental impact of the Felicity Ace incident and to develop strategies for mitigating the damage. These efforts include monitoring water and air quality, assessing the health of marine life, and developing plans for cleaning up any oil spills or seabed contamination. The incident serves as a reminder of the potential environmental risks associated with the transportation of hazardous materials by sea and the need for improved safety measures and emergency response protocols.
Economic Impact
The Felicity Ace incident has had a significant economic impact on a variety of stakeholders, including:
-
Automakers: Volkswagen, Porsche, Audi, Bentley, and Lamborghini were among the automakers with vehicles on board the Felicity Ace. These companies faced significant financial losses due to the destruction of their vehicles. The incident also disrupted their supply chains and potentially affected their sales and revenue.
-
Shipping Companies: The company responsible for operating the Felicity Ace faced significant costs associated with the incident, including salvage operations, environmental cleanup, and potential liability claims. The incident also damaged their reputation and potentially affected their future business prospects.
-
Insurance Companies: Insurance companies were responsible for covering the losses associated with the Felicity Ace incident, including the cost of the vehicles, the salvage operations, and the environmental cleanup. The incident resulted in significant payouts for insurance companies and potentially affected insurance premiums for future shipments of vehicles.
-
Consumers: Consumers who had ordered vehicles that were on board the Felicity Ace faced delays in receiving their orders. Some consumers may have had to reorder their vehicles or choose alternative models. The incident also potentially affected the resale value of similar vehicles.
-
Salvage Companies: Salvage companies were hired to attempt to salvage the Felicity Ace and its cargo. These companies earned revenue from their salvage operations, but they also faced significant risks and challenges due to the intense heat and unstable condition of the ship.
-
Environmental Cleanup Companies: Environmental cleanup companies may have been hired to clean up any oil spills or seabed contamination resulting from the Felicity Ace incident. These companies earned revenue from their cleanup operations.
-
Local Economy: The Felicity Ace incident potentially affected the local economy in the Azores, where the ship caught fire. The incident could have affected tourism, fishing, and other industries.
The economic impact of the Felicity Ace incident is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars. The incident serves as a reminder of the potential economic risks associated with the transportation of goods by sea and the need for effective risk management strategies.
FAQ Section
1. What caused the fire on the Felicity Ace?
The exact cause of the fire is still under investigation. However, initial reports suggested that lithium-ion batteries in the electric vehicles on board may have contributed to the intensity and persistence of the blaze. Lithium-ion batteries are known to be flammable and can be difficult to extinguish once ignited. The investigation is ongoing to determine the precise origin and cause of the fire.
2. What types of vehicles were on board the Felicity Ace?
The Felicity Ace was carrying approximately 4,000 vehicles, including models from Volkswagen, Porsche, Audi, Bentley, and Lamborghini. A significant portion of these vehicles were electric vehicles (EVs), which contain lithium-ion batteries.
3. What is the environmental impact of the Felicity Ace sinking?
The environmental impact is multifaceted. The burning of the ship released toxic fumes into the atmosphere, potentially affecting air quality and marine life. The sinking of the ship poses a risk of oil spills and seabed contamination from fuel oil and vehicle components. The presence of lithium-ion batteries adds another layer of complexity, as the chemicals they contain can be harmful to marine ecosystems. Long-term monitoring and assessment are needed to fully understand the extent of the environmental damage.
4. What are the safety regulations for transporting lithium-ion batteries by sea?
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has regulations for the safe transport of dangerous goods by sea, including lithium-ion batteries. These regulations cover packaging, labeling, stowage, and firefighting. However, some experts argue that these regulations may not be comprehensive enough to address the specific risks associated with transporting large quantities of lithium-ion batteries, especially in electric vehicles. There is ongoing debate about the adequacy of these regulations and whether they need to be updated.
5. What is being done to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future?
The Felicity Ace incident has prompted calls for a review of the regulations governing the transport of lithium-ion batteries by sea. Suggestions include stricter regulations on packaging and stowage, improved firefighting capabilities on cargo ships, and more research into safer battery technologies and firefighting techniques. Collaboration between regulators, industry stakeholders, and researchers is crucial to develop and implement more effective safety measures. This may also include improved detection and suppression systems specific to lithium-ion battery fires on cargo ships.