Potential tariffs on Chinese-made auto parts and vehicles could disproportionately impact several car brands, potentially leading to significant price increases for consumers, according to a recent report. Volvo, Buick, and Polestar are identified as brands facing the most substantial risk due to their reliance on Chinese manufacturing.
These brands could experience the steepest price increases if proposed tariffs on Chinese imports, particularly auto parts, are implemented. The Peterson Institute for International Economics analysis indicates that tariffs could lead to broad price increases across the automotive market, affecting both imported vehicles and those assembled in the United States with imported components. This situation arises from ongoing trade tensions and efforts to reshape global supply chains.
The tariffs under consideration aim to incentivize domestic production and reduce reliance on Chinese manufacturing. However, the immediate impact would likely be higher costs for consumers. Volvo, owned by Chinese company Geely, imports all its U.S.-bound vehicles from China. Buick, a General Motors brand, imports its Envision SUV from China. Polestar, also owned by Geely, manufactures its electric vehicles in China for global distribution.
The potential consequences extend beyond specific brands. A broad range of automotive components, from engines to electronics, are sourced from China. Tariffs on these parts could ripple through the industry, affecting vehicles produced by numerous manufacturers, even those with significant U.S. operations.
The complexity of the automotive supply chain means that even vehicles labeled as “American-made” often rely on imported parts, and tariffs on these components would translate into increased production costs. This cost escalation could then be passed on to consumers through higher vehicle prices.
The report highlights a potential conflict between the goals of encouraging domestic manufacturing and maintaining affordable vehicle prices. Policymakers face the challenge of balancing these competing interests as they consider potential trade measures. The effects of these tariffs may influence purchasing decisions, potentially shifting consumer preferences towards brands less reliant on Chinese-made parts and vehicles, if available, and if price differences become significant.
The potential for tariff-induced price hikes raises questions about the long-term competitiveness of affected brands and the overall health of the automotive market. The outcome of these trade policy debates will likely have significant implications for both manufacturers and consumers.
Brand-Specific Vulnerabilities
Volvo faces the greatest risk because it imports all of its U.S.-bound vehicles from China. Geely’s decision to manufacture Volvo vehicles in China for export to the U.S. market made sense at the time, due to lower production costs. However, this strategy now makes Volvo particularly vulnerable to tariffs. If tariffs are imposed, Volvo may be forced to raise prices significantly, potentially impacting sales volume and market share in the U.S.
Buick, despite being a General Motors brand with a long history of American manufacturing, imports its Envision SUV from China. This decision reflects the global nature of automotive production, where manufacturers seek the most cost-effective locations for specific models. However, the Envision’s reliance on Chinese manufacturing exposes Buick to potential tariff-related price increases. GM would need to assess whether absorbing the tariff costs, shifting production, or passing the increases on to consumers would be the most viable strategy.
Polestar, an electric vehicle brand, manufactures all of its vehicles in China. As a relatively new entrant in the electric vehicle market, Polestar is particularly sensitive to price changes. Tariffs could make Polestar vehicles less competitive compared to other electric vehicles produced in countries without tariffs. Polestar could consider diversifying its production base to mitigate this risk, but this would require significant investment and time.
Impact on the Broader Automotive Market
The potential impact of tariffs extends beyond these three brands. Many other automakers rely on Chinese-made parts for vehicles assembled in the United States. Tariffs on these parts would increase production costs for these manufacturers as well.
The automotive industry operates on a complex and interconnected global supply chain. Even vehicles that are labeled as “American-made” often contain a significant percentage of imported parts. For example, a car assembled in the United States might have an engine, transmission, or electronic components manufactured in China. Tariffs on these components would increase the overall cost of producing the vehicle.
Automakers might respond to these cost increases in a variety of ways. They could try to absorb the costs themselves, reducing their profit margins. They could try to find alternative suppliers in other countries, but this could be a lengthy and expensive process. Or, they could pass the costs on to consumers in the form of higher vehicle prices.
The most likely scenario is that automakers will use a combination of these strategies. They might absorb some of the costs, find alternative suppliers for some parts, and raise prices on some vehicles. The precise impact on consumers will depend on the specific strategies that automakers choose to pursue.
Economic and Geopolitical Context
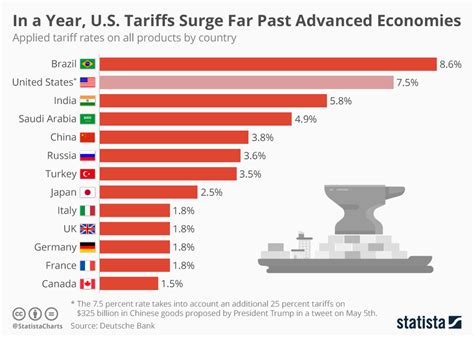
The potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles are part of a broader trade dispute between the United States and China. The U.S. government has imposed tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods in recent years, and China has retaliated with tariffs on U.S. goods.
The stated goals of these tariffs are to protect American jobs, reduce the trade deficit, and encourage China to change its trade practices. However, the tariffs have also led to higher prices for consumers and businesses, and they have disrupted global supply chains.
The automotive industry has been particularly affected by these trade tensions. Automakers rely on complex and global supply chains, and tariffs can disrupt these supply chains and increase costs.
The potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles could further escalate trade tensions between the United States and China. It is possible that China could retaliate with its own tariffs on U.S. goods. This could lead to a further disruption of global trade and investment.
Alternative Strategies for Automakers
Faced with the prospect of higher tariffs, automakers are exploring alternative strategies to mitigate the impact on their businesses. These strategies include:
- Shifting Production: Automakers could shift production of vehicles and parts from China to other countries. This would involve significant investment in new factories and equipment, but it would reduce their exposure to tariffs. For example, Volvo could shift some of its production to Europe or North America.
- Finding Alternative Suppliers: Automakers could find alternative suppliers of parts in other countries. This would require a significant effort to identify and qualify new suppliers, but it would reduce their reliance on Chinese-made parts.
- Absorbing Costs: Automakers could choose to absorb some of the tariff costs themselves, rather than passing them on to consumers. This would reduce their profit margins, but it would help to maintain their competitiveness in the market.
- Raising Prices: Automakers could raise prices on their vehicles to offset the higher costs of tariffs. This would make their vehicles less affordable for consumers, but it would protect their profit margins.
- Lobbying for Tariff Relief: Automakers could lobby the government to reduce or eliminate the tariffs. This would require a concerted effort to persuade policymakers that the tariffs are harmful to the industry and to consumers.
The effectiveness of these strategies will depend on the specific circumstances of each automaker. Some automakers may be better positioned to shift production or find alternative suppliers than others. Some automakers may be more willing to absorb costs or raise prices than others.
Impact on Consumers
The potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles could have a significant impact on consumers. Higher prices for vehicles would make it more difficult for people to afford transportation. This could disproportionately affect low-income consumers, who are already struggling to make ends meet.
The tariffs could also lead to a reduction in the availability of certain types of vehicles. If automakers are forced to raise prices on vehicles that are made in China or that contain Chinese-made parts, they may choose to discontinue those models. This would reduce the choices available to consumers.
The tariffs could also slow the transition to electric vehicles. Electric vehicles are often more expensive than gasoline-powered vehicles, and tariffs could make them even more expensive. This could make it more difficult for consumers to switch to electric vehicles, which would slow the adoption of cleaner transportation technologies.
Policy Implications
The potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles raise important policy questions. Policymakers must weigh the potential benefits of the tariffs, such as protecting American jobs and reducing the trade deficit, against the potential costs, such as higher prices for consumers and a disruption of global supply chains.
Policymakers must also consider the potential impact of the tariffs on the automotive industry. The automotive industry is a major employer in the United States, and tariffs could harm the industry and lead to job losses.
Policymakers must also consider the potential impact of the tariffs on the transition to electric vehicles. Electric vehicles are essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change, and tariffs could slow the adoption of electric vehicles.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to impose tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles is a complex one with significant economic and political implications. Policymakers must carefully consider all of the potential costs and benefits before making a decision.
Looking Ahead
The situation remains dynamic, with the future of tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles uncertain. Negotiations between the U.S. and China could lead to a resolution that avoids the imposition of tariffs, or the tariffs could be implemented as proposed.
Regardless of the outcome, the potential for tariffs highlights the risks associated with relying on a single country for critical components of the automotive supply chain. Automakers are likely to continue to diversify their supply chains and explore alternative production locations in order to mitigate these risks.
Consumers should be aware of the potential for higher vehicle prices and reduced vehicle availability as a result of tariffs. They may want to consider purchasing vehicles from brands that are less reliant on Chinese-made parts and vehicles.
The automotive industry is undergoing a period of significant change, driven by technological innovation, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving trade policies. The potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles are just one of the many challenges facing the industry. Automakers that are able to adapt to these changes will be best positioned to succeed in the future.
Conclusion
The imposition of tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles could have significant consequences for automakers and consumers. Volvo, Buick, and Polestar are particularly vulnerable due to their reliance on Chinese manufacturing. The tariffs could lead to higher vehicle prices, reduced vehicle availability, and a slowdown in the transition to electric vehicles.
Policymakers face a difficult decision in weighing the potential benefits of the tariffs against the potential costs. Automakers are exploring alternative strategies to mitigate the impact of the tariffs on their businesses. The future of the automotive industry will depend on how these challenges are addressed. The ripple effect of these decisions can extend to global markets, significantly impacting the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Which car brands are most likely to be affected by potential tariffs on Chinese auto parts and vehicles?
According to the Yahoo Finance article, Volvo, Buick, and Polestar are identified as the brands facing the biggest potential price hikes due to their reliance on manufacturing or sourcing components from China. Volvo imports all its U.S.-bound vehicles from China, Buick imports its Envision SUV, and Polestar manufactures its electric vehicles there.
2. Why are these specific brands more vulnerable than others?
These brands are more vulnerable because of their existing manufacturing and import strategies. Volvo’s entire U.S. lineup is imported from China. Buick sources a specific model, the Envision, from China, and Polestar’s production is entirely based in China. This level of dependence on Chinese production means tariffs would directly translate into increased costs.
3. What are the potential consequences of these tariffs for consumers?
Consumers could face higher vehicle prices if tariffs are implemented. This would make cars more expensive, potentially impacting sales volume and market share for affected brands. It could also influence consumer purchasing decisions, possibly shifting preferences towards brands that are less reliant on Chinese manufacturing.
4. Beyond these brands, how could tariffs impact the broader automotive market?
Many automakers rely on Chinese-made parts for vehicles assembled in the United States. Tariffs on these parts would increase production costs, affecting vehicles produced by numerous manufacturers, even those with significant U.S. operations. This could lead to price increases across a wide range of vehicles, not just those imported directly from China.
5. What alternative strategies can automakers use to mitigate the impact of these tariffs?
Automakers could consider several strategies, including:
- Shifting production: Moving manufacturing out of China to other countries.
- Finding alternative suppliers: Sourcing parts from countries other than China.
- Absorbing costs: Reducing profit margins to keep prices competitive.
- Raising prices: Passing the increased costs on to consumers.
- Lobbying for tariff relief: Engaging in political efforts to reduce or eliminate the tariffs.
6. What is the current geopolitical context driving these potential tariffs?
The potential tariffs are part of an ongoing trade dispute between the United States and China. The U.S. government aims to protect American jobs, reduce the trade deficit, and encourage China to change its trade practices. However, these tariffs have also led to higher prices and disrupted global supply chains.
7. How might the tariffs affect the transition to electric vehicles (EVs)?
Tariffs could slow the transition to EVs by making them more expensive. Since EVs often have higher initial costs than gasoline-powered vehicles, tariffs could further increase their prices, making them less accessible to consumers. This could impede the adoption of cleaner transportation technologies.
8. Are vehicles labeled “American-made” immune to these tariff effects?
No, even vehicles labeled “American-made” often rely on imported parts, including those from China. Tariffs on these imported components would increase the overall cost of producing the vehicle, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers, regardless of where the final assembly takes place.
9. What role does Geely play in the vulnerability of Volvo and Polestar?
Geely, a Chinese company, owns both Volvo and Polestar. This ownership and the decision to manufacture vehicles in China for export to the U.S. market have made these brands particularly susceptible to tariffs. Geely’s strategic decisions regarding manufacturing locations directly influence the brands’ tariff exposure.
10. How could the implementation of these tariffs affect the United States’ trade relationship with China?
The tariffs could further escalate trade tensions between the United States and China. China might retaliate with its own tariffs on U.S. goods, leading to a further disruption of global trade and investment. This reciprocal action could have broad economic consequences beyond the automotive industry.
11. What is the Peterson Institute for International Economics’ assessment of the situation?
The Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE) conducted an analysis indicating that tariffs could lead to broad price increases across the automotive market, affecting both imported vehicles and those assembled in the United States with imported components. Their research highlights the potential for widespread economic impact.
12. How does the complexity of the automotive supply chain contribute to the potential price increases?
The automotive industry operates on a complex and interconnected global supply chain. This intricacy means that even seemingly small tariffs on specific components can have a cascading effect, impacting multiple stages of production and ultimately leading to higher costs for consumers.
13. What are some long-term strategies automakers might adopt in response to these potential tariffs?
Automakers could pursue long-term strategies such as:
- Reshoring: Bringing manufacturing back to the United States.
- Nearshoring: Moving production to countries closer to the United States, such as Mexico or Canada.
- Diversifying suppliers: Building relationships with suppliers in multiple countries to reduce reliance on any single source.
- Investing in automation: Reducing labor costs to offset the impact of tariffs.
14. What kind of lobbying efforts might automakers undertake to address the tariffs?
Automakers might engage in lobbying efforts to:
- Educate policymakers: Informing government officials about the potential negative impacts of tariffs on the industry and consumers.
- Advocate for tariff exemptions: Seeking specific exemptions for certain parts or vehicles.
- Support trade negotiations: Encouraging the U.S. government to negotiate a trade agreement with China that eliminates or reduces tariffs.
- Highlight job creation: Emphasizing the role of the automotive industry in creating jobs in the United States.
15. How do these tariffs align with the U.S. government’s broader economic goals?
The tariffs are intended to align with the U.S. government’s goals of:
- Protecting domestic industries: Shielding American manufacturers from foreign competition.
- Reducing the trade deficit: Decreasing the amount by which U.S. imports exceed U.S. exports.
- Encouraging domestic production: Incentivizing companies to manufacture goods in the United States.
- Strengthening national security: Reducing reliance on foreign suppliers for critical goods and components.
16. What are the potential risks of shifting production out of China?
Shifting production out of China can involve risks such as:
- Higher labor costs: Labor costs may be higher in other countries.
- Supply chain disruptions: Establishing new supply chains can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Loss of expertise: Moving production may result in the loss of skilled workers and specialized knowledge.
- Geopolitical instability: Other countries may also be subject to geopolitical risks.
17. How might consumers adjust their purchasing habits in response to higher vehicle prices?
Consumers might adjust their purchasing habits by:
- Delaying purchases: Postponing the purchase of a new vehicle.
- Buying used vehicles: Opting for a pre-owned vehicle instead of a new one.
- Downsizing: Choosing a smaller, more affordable vehicle.
- Switching brands: Selecting a brand that is less affected by tariffs.
- Leasing: Leasing a vehicle instead of buying it outright.
18. What role do government subsidies play in mitigating the impact of tariffs?
Government subsidies can help to mitigate the impact of tariffs by:
- Reducing production costs: Providing financial assistance to manufacturers to offset the higher costs of production due to tariffs.
- Incentivizing domestic production: Offering tax breaks or other incentives to encourage companies to manufacture goods in the United States.
- Supporting research and development: Funding research and development of new technologies that can reduce production costs or improve the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers.
19. What are the potential consequences of a trade war between the United States and China?
A trade war between the United States and China could have significant consequences, including:
- Higher prices for consumers: Tariffs would increase the cost of goods imported from both countries.
- Reduced economic growth: Trade disruptions could slow economic growth in both countries and globally.
- Job losses: Companies that rely on trade between the two countries could be forced to lay off workers.
- Increased uncertainty: Trade disputes can create uncertainty for businesses, making it difficult to plan for the future.
20. What are the potential benefits of the tariffs for the U.S. automotive industry?
Potential benefits for the U.S. automotive industry might include:
- Increased domestic production: Encouraging automakers to manufacture more vehicles and parts in the United States.
- Job creation: Creating new jobs in the automotive industry.
- Strengthened supply chains: Reducing reliance on foreign suppliers and building more resilient domestic supply chains.
- Improved competitiveness: Helping U.S. automakers compete more effectively with foreign manufacturers.



![[Restaurant Name] Returns! Iconic Chain Revives After 30-Year Absence](https://generasitekno.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/unnamed-file-924-150x150.jpg)





