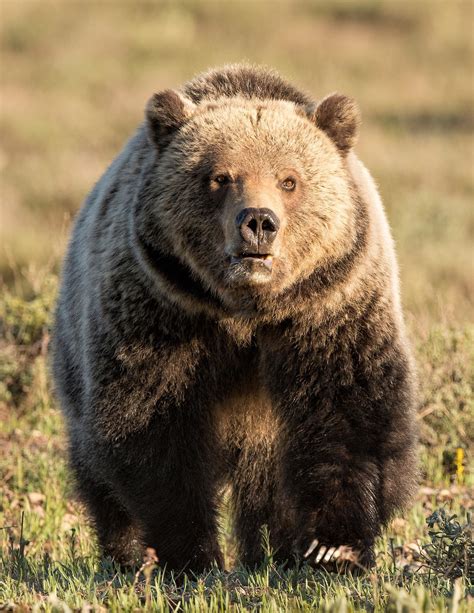
A remarkable video captured in Montana showcases a grizzly bear running at full speed across an open field, stunning viewers with its agility and power. The short clip, shared widely on social media, provides a rare glimpse into the raw athleticism of these apex predators in their natural habitat.
The video, recorded recently, shows the bear moving at an impressive pace across the landscape, highlighting its physical capabilities. According to reports, the bear’s demonstration of speed serves as a potent reminder of the animal’s inherent power and its ability to cover ground quickly when necessary.
The incident has sparked significant interest and discussion among wildlife enthusiasts and the general public alike, emphasizing the importance of understanding and respecting the power and capabilities of grizzly bears.
Montana Grizzly Bear’s Sprint Captured on Video, Showcasing Raw Power and Agility
A recently captured video in Montana has gone viral, showcasing a grizzly bear running at full speed across an open field, leaving viewers in awe of its power and agility. The short clip offers a rare and captivating glimpse into the raw athleticism of these apex predators in their natural environment. The display of speed serves as a potent reminder of the animal’s inherent power and its ability to traverse distances swiftly.
The video, shared widely across social media platforms, has sparked considerable interest and discussion among wildlife enthusiasts, conservationists, and the general public, underscoring the need to understand and respect the power and capabilities of grizzly bears.
The exact location where the video was filmed has not been publicly disclosed to protect the bear and its habitat. However, the footage clearly shows the grizzly in a natural setting, far from human development. The bear’s motivations for running at such a high speed remain speculative, but possible explanations include pursuing prey, responding to a perceived threat, or simply expending energy.
Experts suggest that grizzly bears can reach speeds of up to 35 miles per hour in short bursts. This speed rivals that of some horses and makes them one of the fastest land animals of their size. Their powerful muscles and large paws enable them to accelerate quickly and maintain high speeds over short distances.
The incident serves as a reminder of the importance of practicing bear safety in grizzly country. Authorities recommend carrying bear spray, making noise while hiking, and storing food properly to avoid attracting bears. Encounters with grizzly bears can be dangerous, and it is crucial to take precautions to minimize the risk of conflict.
The widespread attention the video has garnered highlights the ongoing fascination with grizzly bears and their place in the North American wilderness. These magnificent creatures play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitat, and their conservation is essential for preserving biodiversity.
Detailed Analysis of the Video and Grizzly Bear Behavior
The viral video provides an opportunity to examine the physical attributes and behavioral characteristics that make grizzly bears such formidable creatures. Grizzly bears ( Ursus arctos horribilis) are a subspecies of the brown bear, native to North America. They are characterized by their large size, distinctive shoulder hump, and long claws, which are well-suited for digging and foraging.
Adult male grizzly bears typically weigh between 300 and 800 pounds, while females weigh between 200 and 450 pounds. They can stand up to 8 feet tall on their hind legs. Their thick fur provides insulation against the harsh weather conditions of their habitat, which includes forests, meadows, and alpine regions.
The shoulder hump, a prominent feature of grizzly bears, is composed of muscle and fat and provides them with the strength needed for digging and overturning rocks in search of food. Their long claws, which can measure up to 4 inches in length, are used for digging up roots, tubers, and burrowing animals.
Grizzly bears are omnivores, with a diet that consists of a wide variety of plants and animals. They feed on berries, roots, grasses, insects, fish, and mammals, including elk, deer, and moose. Their diet varies depending on the season and the availability of food resources.
During the fall, grizzly bears enter a period of hyperphagia, during which they consume large quantities of food to build up fat reserves for the winter. They can gain several pounds of weight per day during this time. In the winter, they enter a state of dormancy, during which their metabolism slows down and they rely on their stored fat reserves for energy. They do not hibernate in the true sense of the word, as their body temperature does not drop significantly, and they can awaken easily if disturbed.
Grizzly bears are solitary animals, except for females with cubs. They have a large home range, which can vary from several square miles to hundreds of square miles, depending on the availability of food and other resources. They communicate with each other through scent marking, vocalizations, and body language.
The video of the grizzly bear running at full speed demonstrates the impressive physical capabilities of these animals. Their powerful muscles and large paws enable them to accelerate quickly and maintain high speeds over short distances. They are also adept at navigating uneven terrain and climbing trees.
Grizzly bears are known for their unpredictable behavior and can be dangerous if they feel threatened or if they are protecting their cubs. They have a strong sense of smell and can detect food from a great distance. It is important to store food properly and avoid attracting them to human settlements.
Encounters with grizzly bears are relatively rare, but they can occur in areas where their habitat overlaps with human development. It is important to be aware of bear safety guidelines and to take precautions to minimize the risk of conflict. These guidelines include carrying bear spray, making noise while hiking, and avoiding hiking alone.
Conservation Status and Challenges Facing Grizzly Bears
Grizzly bears were once widespread throughout North America, but their population has declined significantly due to habitat loss, hunting, and other human activities. They are currently listed as a threatened species in the contiguous United States, with populations in Montana, Wyoming, Idaho, and Washington.
The Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem (GYE), which includes Yellowstone National Park and the surrounding areas, is home to one of the largest and most well-studied grizzly bear populations in the United States. The GYE grizzly bear population has recovered significantly since the 1970s, when it was estimated to be as low as 136 bears. Today, the population is estimated to be over 700 bears.
However, grizzly bears still face a number of challenges, including habitat loss, human-caused mortality, and climate change. Habitat loss is a major threat to grizzly bears, as it reduces the availability of food and other resources. Human-caused mortality, including hunting, poaching, and vehicle collisions, is another significant threat.
Climate change is also expected to have a negative impact on grizzly bears, as it could alter their habitat and food sources. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns could affect the distribution and abundance of berries, roots, and other plants that grizzly bears rely on for food. Climate change could also lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires, which could destroy grizzly bear habitat.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect grizzly bears and their habitat. These efforts include habitat restoration, conflict prevention, and public education. Habitat restoration projects aim to improve the quality and availability of grizzly bear habitat by restoring degraded areas and removing barriers to movement.
Conflict prevention efforts focus on reducing the risk of human-bear conflicts by educating people about bear safety and promoting the use of bear-resistant food storage containers. Public education programs aim to increase awareness of grizzly bears and their importance to the ecosystem.
The successful recovery of the GYE grizzly bear population demonstrates that conservation efforts can be effective in protecting these magnificent creatures. However, continued vigilance and proactive management are essential to ensure their long-term survival.
The Role of Technology in Wildlife Monitoring and Conservation
The viral video of the grizzly bear running at full speed highlights the increasing role of technology in wildlife monitoring and conservation. Camera traps, GPS collars, and other technologies are providing researchers with valuable data on animal behavior, movements, and population dynamics.
Camera traps are remotely triggered cameras that are used to capture images or videos of animals. They are often placed in areas where animals are known to frequent, such as trails, watering holes, and feeding areas. Camera traps can provide valuable information on animal activity patterns, habitat use, and population size.
GPS collars are used to track the movements of animals over time. They are attached to animals and transmit data on their location to researchers via satellite. GPS collars can provide information on animal home ranges, migration routes, and habitat use.
Other technologies, such as drones and acoustic monitoring devices, are also being used to monitor wildlife populations. Drones can be used to survey large areas of habitat and to collect data on animal distribution and abundance. Acoustic monitoring devices can be used to record animal vocalizations and to track their movements.
The data collected using these technologies can be used to inform conservation management decisions and to assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts. For example, GPS collar data can be used to identify important habitat areas that need to be protected. Camera trap data can be used to monitor population trends and to assess the impact of human activities on wildlife populations.
The use of technology in wildlife monitoring and conservation is rapidly expanding, and it is expected to play an increasingly important role in the future. As technology advances, it will become even easier and more cost-effective to collect data on wildlife populations. This data will be essential for informing conservation management decisions and for ensuring the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures.
The Ethical Considerations of Wildlife Photography and Videography
While the video of the running grizzly bear has captured the public’s imagination, it also raises important ethical considerations about wildlife photography and videography. It is essential to balance the desire to document and share these animals with the need to protect their well-being and minimize disturbance to their natural behavior.
Ethical wildlife photography and videography practices prioritize the welfare of the animals and their environment. This includes minimizing disturbance, avoiding habituation, and respecting their space. It is crucial to never approach animals too closely, especially during sensitive times such as mating season or when they have young.
Habituation, which occurs when animals become accustomed to human presence and lose their natural fear, can have negative consequences. Habituated animals may become more vulnerable to poachers, less wary of vehicles, and more likely to approach humans for food, leading to potential conflicts.
It is also important to avoid altering the environment to attract or photograph animals. This includes baiting, which can disrupt their natural feeding patterns and create dependence on humans. Similarly, manipulating vegetation or other natural features can disturb their habitat and disrupt their behavior.
Responsible wildlife photographers and videographers adhere to a strict code of ethics that emphasizes respect for the animals and their environment. They educate themselves about the species they are photographing and their specific needs. They also obtain necessary permits and follow all regulations.
Furthermore, ethical wildlife photographers and videographers use their images and videos to promote conservation and raise awareness about the challenges facing wildlife populations. They share their work with conservation organizations and use it to educate the public about the importance of protecting these animals and their habitat.
The video of the running grizzly bear serves as a reminder of the power and beauty of these animals, but it also underscores the need to approach wildlife photography and videography with responsibility and respect. By adhering to ethical principles, we can ensure that these activities do not harm the animals we are trying to capture on film.
The Broader Ecological Significance of Grizzly Bears
Grizzly bears play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological health and biodiversity of their habitat. As apex predators, they regulate prey populations, influence plant communities, and contribute to nutrient cycling. Their presence in an ecosystem is an indicator of its overall health and stability.
Grizzly bears help to control populations of ungulates such as elk, deer, and moose. By preying on these animals, they prevent overgrazing and maintain a balance between herbivores and plant communities. This, in turn, supports a diverse range of plant species and the animals that depend on them.
Grizzly bears also contribute to nutrient cycling by dispersing seeds and distributing nutrients throughout their habitat. They consume large quantities of berries and other fruits, and the undigested seeds are dispersed in their scat, helping to regenerate plant communities. They also dig up roots and tubers, which aerates the soil and promotes plant growth.
In addition, grizzly bears play a role in scavenging carrion, which helps to prevent the spread of disease and maintain the health of the ecosystem. They consume the carcasses of dead animals, which would otherwise decompose and potentially spread pathogens.
The presence of grizzly bears can also have indirect effects on plant communities. For example, their digging activities can create small-scale disturbances that promote plant diversity. They also influence the behavior of other animals, such as wolves and coyotes, which may avoid areas where grizzly bears are present.
The ecological significance of grizzly bears highlights the importance of conserving their populations and protecting their habitat. By maintaining healthy grizzly bear populations, we can ensure the long-term health and stability of the ecosystems they inhabit.
The Importance of Bear Safety in Grizzly Bear Country
The viral video of the grizzly bear’s impressive sprint serves as a timely reminder of the importance of practicing bear safety in areas inhabited by these powerful animals. Encounters with grizzly bears, while relatively rare, can be dangerous, and it is crucial to take precautions to minimize the risk of conflict.
Bear safety practices are designed to prevent encounters with bears and to reduce the likelihood of a negative outcome if an encounter does occur. These practices include storing food properly, making noise while hiking, carrying bear spray, and knowing how to react if you encounter a bear.
Food storage is one of the most important aspects of bear safety. Bears have a strong sense of smell and can be attracted to human food from great distances. It is essential to store food in bear-resistant containers or to hang it from a tree at least 10 feet off the ground and 4 feet from the trunk.
Making noise while hiking can help to alert bears to your presence and give them time to avoid you. This can be done by talking loudly, singing, or carrying a bell. Hiking in groups is also recommended, as bears are less likely to approach a group of people.
Carrying bear spray is another essential component of bear safety. Bear spray is a powerful deterrent that can be used to stop a bear attack. It is important to know how to use bear spray properly and to carry it in an easily accessible location.
If you encounter a bear, it is important to remain calm and assess the situation. If the bear is unaware of your presence, slowly back away and leave the area. If the bear is aware of your presence, speak in a calm voice and wave your arms. Do not run, as this may trigger the bear’s predatory instincts.
If the bear approaches you, stand your ground and prepare to use your bear spray. If the bear attacks, deploy your bear spray and aim for its face. Once the bear has been deterred, slowly back away and leave the area.
By following these bear safety practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of a negative encounter with a grizzly bear and help to ensure your safety in bear country.
The Cultural Significance of Grizzly Bears to Indigenous Peoples
Grizzly bears hold a profound cultural and spiritual significance for many Indigenous peoples in North America. They are often viewed as powerful and respected beings, embodying qualities such as strength, courage, and wisdom.
In many Indigenous cultures, grizzly bears are considered to be relatives or ancestors. They are often featured in stories, legends, and ceremonies, and their images are incorporated into art, clothing, and other cultural artifacts.
Grizzly bears are also seen as symbols of healing and protection. Their claws and teeth are sometimes used in traditional medicine, and their images are often displayed in homes and sacred places to ward off evil spirits.
The relationship between Indigenous peoples and grizzly bears is deeply intertwined with their traditional way of life. For centuries, Indigenous peoples have relied on grizzly bears for food, clothing, and other resources. They have also developed a deep understanding of bear behavior and ecology, which has been passed down through generations.
In recent years, Indigenous communities have played an increasingly important role in grizzly bear conservation. They have worked with government agencies and other organizations to develop and implement management plans that protect bear populations and respect Indigenous cultural values.
The cultural significance of grizzly bears highlights the importance of engaging Indigenous peoples in conservation efforts and of recognizing their traditional knowledge and perspectives. By working together, we can ensure the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures and honor their cultural importance.
The Future of Grizzly Bear Conservation
The future of grizzly bear conservation depends on a number of factors, including habitat protection, conflict prevention, and climate change mitigation. Continued efforts are needed to protect and restore grizzly bear habitat, to reduce the risk of human-bear conflicts, and to address the impacts of climate change on bear populations.
Habitat protection is essential for ensuring that grizzly bears have access to the food, shelter, and other resources they need to survive. This includes protecting existing habitat from development and fragmentation and restoring degraded habitat through reforestation and other conservation practices.
Conflict prevention efforts are needed to reduce the risk of human-bear conflicts, which can lead to bear mortality. This includes educating people about bear safety, promoting the use of bear-resistant food storage containers, and implementing strategies to reduce bear attraction to human settlements.
Climate change mitigation is also essential for ensuring the long-term survival of grizzly bears. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing strategies to adapt to the impacts of climate change on bear habitat and food sources.
In addition, continued research and monitoring are needed to track grizzly bear populations and to assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts. This includes using GPS collars to track bear movements, camera traps to monitor population trends, and genetic analysis to assess population health.
The future of grizzly bear conservation will require a collaborative effort involving government agencies, conservation organizations, Indigenous communities, and the public. By working together, we can ensure that these magnificent creatures continue to thrive in the North American wilderness for generations to come.
FAQ: Grizzly Bear News and Conservation
-
How fast can a grizzly bear actually run?
Grizzly bears can reach speeds of up to 35 miles per hour in short bursts. As the rewritten article states, “Experts suggest that grizzly bears can reach speeds of up to 35 miles per hour in short bursts. This speed rivals that of some horses and makes them one of the fastest land animals of their size.”
-
What should I do if I encounter a grizzly bear while hiking?
If you encounter a grizzly bear, remain calm, speak in a calm voice, and wave your arms. Do not run. If the bear approaches, stand your ground and prepare to use bear spray. Back away slowly while facing the bear. According to the rewritten article: “If you encounter a bear, it is important to remain calm and assess the situation. If the bear is unaware of your presence, slowly back away and leave the area. If the bear is aware of your presence, speak in a calm voice and wave your arms. Do not run, as this may trigger the bear’s predatory instincts.”
-
Where is it safe to see bears in Montana?
Reliable sources say that Yellowstone National Park and Glacier National Park are considered prime locations to view grizzly bears safely from a distance. However, respecting wildlife and keeping your distance is critical. It’s important to be aware of your surroundings and follow park regulations.
-
Why are grizzly bear populations considered threatened?
Grizzly bear populations are considered threatened due to habitat loss, human-caused mortality (including hunting and vehicle collisions), and the effects of climate change. As stated in the rewritten article, “Grizzly bears were once widespread throughout North America, but their population has declined significantly due to habitat loss, hunting, and other human activities. They are currently listed as a threatened species in the contiguous United States, with populations in Montana, Wyoming, Idaho, and Washington.”
-
What is bear spray and how effective is it?
Bear spray is a powerful deterrent made from capsaicin, a derivative of chili peppers. It is designed to temporarily incapacitate a bear, giving you time to escape. It is considered highly effective when used correctly. The rewritten article mentions that, “Carrying bear spray is another essential component of bear safety. Bear spray is a powerful deterrent that can be used to stop a bear attack. It is important to know how to use bear spray properly and to carry it in an easily accessible location.”